Here we will explore the drawbacks and limitations of trenchless sewer line repair methods. While these techniques have gained popularity in recent years, it is important to understand their limitations and potential risks before deciding whether to opt for this type of repair.
Understanding Trenchless Sewer Line Repair
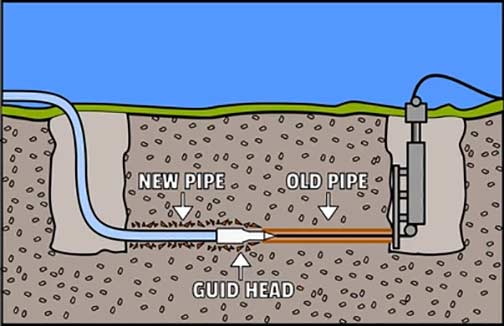
Before getting into the reasons why trenchless sewer line repair may not be a good idea, let’s briefly understand what it entails. This method of sewer line repair is a technique used to fix damaged or deteriorating sewer lines without the need for extensive excavation. It involves inserting a liner or a pipe within the existing sewer line, effectively creating a new, structurally sound pipeline inside the old one.
The Drawbacks of Trenchless Sewer Line Repair
While this method sewer line repair may seem like an attractive option due to its minimal excavation requirements and shorter turnaround time, it is crucial to consider its drawbacks and limitations. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
Limited Suitability
Trenchless sewer line repair is not suitable for all types of sewer line damages. It is most effective for fixing minor cracks, leaks, or corrosion along the pipes. However, if the sewer line has collapsed or suffered severe damage, traditional sewer line replacement methods may be the only viable solution. The limited suitability of trenchless repair can result in additional expenses if the method fails to address the underlying issue.
Potential for Future Issues
While this method sewer line repair may provide a temporary fix, it is important to note that the technique does not address the root cause of the problem. If the sewer line has underlying issues such as tree root intrusion or misaligned pipes, these issues may persist even after a trenchless repair. Neglecting to address these root causes can lead to recurrence of the problem and the need for frequent repairs.
Limited Lifespan
Trenchless sewer line repair methods, such as cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) lining, typically have a limited lifespan compared to traditional excavation and replacement. The liners used in the trenchless process can degrade over time and may require replacement sooner than expected. This can result in additional costs and inconvenience down the line, making trenchless repair a less cost-effective option in the long run.
Potential Environmental Impact
Although trenchless sewer line repair is often touted as an environmentally friendly option, it is worth considering the potential impact it may have. Some trenchless methods involve the use of chemical resins and epoxy materials, which can raise concerns about their environmental safety and long-term effects on water quality. Additionally, inadequate installation or improper disposal of materials used in the trenchless repair process can lead to additional environmental hazards.
Potential for Misdiagnosis
This method of sewer line repair relies on accurate diagnosis of the underlying issue to determine its effectiveness. However, without a thorough sewer camera inspection by experienced plumbers, there is a risk of misdiagnosis. Misidentifying the problem can lead to ineffective repairs, wasted time, and unnecessary expenses. It is crucial to ensure that the chosen repair method aligns with the specific needs of the sewer line.
In Summary
While trenchless sewer line repair may offer certain advantages in terms of reduced excavation and faster turnaround time, it is important to assess its limitations and potential risks. Consider the suitability of trenchless repair for the specific condition of your sewer line, the potential for future issues, the limited lifespan of the repair, the environmental impact, and the risk of misdiagnosis. By weighing these factors, you can make an informed decision about whether this method of sewer line repair is the right choice for your needs.